Article published on Hakin9 IT Security Magazine – August 2012
When we speak about
malware we introduce one of the worst cyber threat that daily evolve with the capacity to hit every sector without distinction. The world “malware” is really generic, we refer in fact a heterogeneous family of malicious software designed with the purpose to disrupt computer operation, gather sensitive information, or gain unauthorized access to victims systems with very different scopes.
Sample of malware type are computer viruses, worms, trojan,
spyware,
ramsonware, adware and rootkits, each of them characterized by an unprecedented growth linked to rapidly changing of the technological context supported by the increased use of internet and the explosion of
mobile services.
The large extension of network like internet and the impressive diffusion of
social networks have advantaged the spread of malicious software, it is to be considered a natural process, to give an idea of what we have observed in the recent years consider that in the last couple of years the release rate of malicious code and of other unwanted programs was greater of the one related to previous 20 years, it’s amazing!
The malware analysis is became an essential component of the security sector, security firms have introduced specific sentinel over the main networks to gather information on every suspect activities that could threaten systems security.
The work is really hard because the malware today have reached a level of sophistication really high, in many cases for their development are engaged teams of experts that work for elude of the principal alerting system, and unfortunately it is happened that some virus or trojan have been discovered years later their diffusion with serious consequences.
How does work the global detection network for malware analysis?
The principal security firms have deployed on the networks thousands of probes used to analyze the traffic and not only, billions email messages and Web requests are processed daily in dedicated data centers, the gathered information are put in relation with data acquired through an antifraud community of enterprises, law enforcement advisor and consumers feedback, only in this way it is possible to detect incoming cyber threat just in time. When user download it’s last antivirus update or anti-rootkit tool he must be aware of the great works that experts do every day without interruption, because malware don’t’ know holidays.
A very interesting part of the precious works done could be appreciated reading the periodical reports that company provides, a precious sources that inform on the incoming threat and related risks. All the data proposed by different analysis of the phenomenon demonstrate a sensible increase of malware diffusion despite the awareness of the cyber threat and the counter measures implemented by private and government entities.
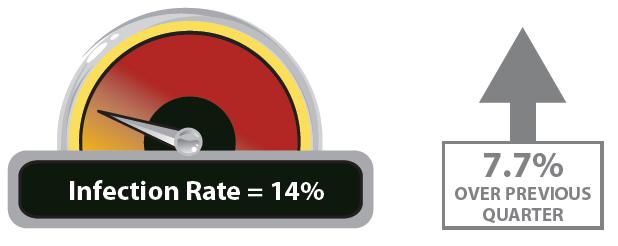
According the data provided by
Kindsight Security, the a majority-owned subsidiary of Alcatel-Lucent, around 14 percent of home networks were infected with malware in the period between April and June 2012.
Figure 1 – Kindsight Security Report – Percentage of home network infected Q2 2012
One of the main vector to spread the malicious agents is still the email, unsuspecting users are daily hijacked on infected website that compromise their machines with various type of malware.
According the proposed statistics 9 percent of residential households were infected by high-threat malware, such as a botnet, rootkit, or a banking Trojan, meanwhile approximately 6 percent were infected with moderate-threat malware such as spyware, browser hijackers, and adware.
Of course in many cases user’s machine is compromised by several malware.
The report dedicates a specific session to the
botnets and in particular to ZeroAccess botnet which grew to over 1.2 million nodes over the second quarter, a figure that could give an idea on the rapidity of the infection diffusion of these agents.
Another primary source of information on the evolution of malware, and more in general of any cyber threat diffusion, related the fights against malware diffusion are the reports and bulletins provided by security firm Symantec. In the last issue of Symantec “Internet Security Threat Report” has been reported an increase respect last year result of a surge in polymorphic malware attacks, particularly from those found in Web attack kits and socially engineered attacks using email-borne malware.
The report giver great emphasis to the increasing of the number of zero day vulnerabilities exploited with a rate of 8 new vulnerabilities per day. Zero-day vulnerabilities represent a serious problem for system security, they are unknown and represents privileged way to avoid security defense of any type of architecture.
Particularly efficient are malicious agent that exploit zero-day vulnerabilities because they could operate being detected also for a long period. According the Symantec data it has been registered an increase of unique variants of malware 140% respect 2010, passing from 286 million of variants to 403 million that confirm the worrying trend.
Malware impact on private and government sectors
We can surely note that malware impact any sector of today society, there is no differences between private business and government affairs, both are very vulnerable to cyber attacks conducted using malicious agents. What is changed in the last couple of years is the awareness that this cyber threat could be used also in military sector. In the last years we have read a lot on the concept of cyber weapon, powerful malware that are used in covert military operation, to compromise enemy’s system.
The possibility to exploit enemy system using a malicious source code is considerable an old idea on which many states have made great investments, but only recently with the massive introduction of technology in everything surround us and the large diffusion of networked systems have made practicable the offensive.
The
Stuxnet case has demonstrated how much powerful could be a cyber weapon and how high is the interest of the governments in the design and development of a malware that is able to interfere with the processes of a critical infrastructure such as a nuclear plant or a telecommunication system.
In a government and military sectors the use of malware is increased in a sensible way, after Stuxnet security company have detected other dangerous instances of malware, Duqu,
Flame and
Mahdi, malicious agent technologically advanced that have been developed with state sponsored project and that mainly have offensive and cyber espionage purposes.
Why a government is interested in the development of a malware for offensive purposes?
- First, the disclosure of such agents is silenced for the nature of the vulnerabilities that are exploited. The study of new zero-day vulnerability provides a real advantage to those who attack and the related risks of failure of operations is minimal. We consider that attacks perpetrated in this way, because of the anonymous nature of the offense, allow you to circumvent the approval by the world community to a military offensive.
- The costs involved in developing solutions such as that at issue are relatively low compared to other conventional weapons.
- The choice of cyber weapon allows those who use the solution to remain anonymous until military strategies deem it appropriate. The main strategies that use of such malware are mainly aimed at:
- Probing the technological capabilities of the enemy. The ability of an agent to infect enemy structures is symptomatic of inadequate cyber defense strategy that may suggest additional military options.
- Undermine those that are considered critical structures whose operation depends on the opponent’s vital functions of the governmental structure of a country.
- No doubt regarding the efficacy of these weapons. Events have proved that they are offensive weapons designed with the intent to infect opposing structures. The cyber weapons can be designed to hit specific targets while minimizing the noise related the usage of the weapon that can result in causing the discovery. The vector of infection can be of various kinds, such as a common USB support, being able to hit a very large number of targets in a small time interval.
- Another significant factor is the ability to predict and to observe the development of a cyber weapon by agencies intelligence. In a classical context the development of a conventional weapon can be easily identified through intelligence operations on the ground and via satellite observations can be easily identified a garrison used to develop military systems. The development of a cyber weapon is rather difficult to locate and thus hinder , even a private home may be suitable for the purpose.
As we have seen the use of malware is becoming very frequent in cyber attacks and cyber espionage campaign but the most evident impact of malware diffusion is without doubt registered in private sectors.
Large organizations register every year billions of dollars of loss related cyber attacks operated using malware, data leaks represents for the businesses one of the primary concerns. Malware could infect computer and entire networks causing serious damage to the productive level of the company. A malware infection could cause the loss of intellectual property or company secrets that could compromise the existence of the business, a malware could also infect production control systems with serious repercussion.
Small business is in my opinion the sector most exposed, small companies due the global crisis have made cost cutting also on security perspective opening the door in many cases to malware and other cyber threat. Lack of resources, reduced budgets and low awareness on cyber threat represents the key factors of a worrying scenario.
Malware diffusion
Security experts have identified various schemes for malware diffusion, of course the mail channel is represented by internet, let’s think to millions of unaware users that daily are infecting simply visiting a compromised web site. The categories of web sites mainly impacted by this type of attack are Blogs & Web communications, Hosting/Personal hosted sites, Business/Economy, Shopping and Education & Reference.
One of the of the most subtle and effective mode of infection is the “Drive-by attacks”, internet users are infected just visiting a compromised website, victims are hijacked on infected websites with very common attack techniques such as ‘clickjacking’ or ‘likejacking’ that deceives the users inducing them to watch a video or simply expressing its pleasure regarding a specific topic using “I like” function.
But the way of malware diffusion are infinite, let’s think to the diffusion on internet of exploit toolkits which allow creation new malware without specific technical capabilities, this peculiarity has facilitated the rapid adoption and diffusion of the attack kits in the criminal world that have intercepted the growing demand in a millionaire business, a phenomenon that continues in its inexorable rise.
The principal channel to spread malware is, according the different security firms, the email. During the last year the number of malicious email is increased targeting mainly large company but also governments and no profit organizations. The infection schema very simple, malicious emails contain infected file as attachment that exploit a vulnerability in the target system, in many targeted attacks to circumvent the user the content of the mail appears legitimate and try to catch the attention of the victim.
In alternative way the email could contains a reference to a compromised web site that host malware able to infect user’s machine.
Using a similar schema for example in Syria and in Tibet governments have spread agents to political persecute opponents tracing their activities and take the remote control of their machine to steal documents and precious information.
But malware could also be diffused through the social networks platforms, they represents digital squares where millions of users exchange videos, images and links, an ideal scenario for the diffusion of malicious code. During the last year with the impressive growth of social network we have also observed the increase of the number of malware propagated using the popular social platforms. Millions of user always connected and with low awareness on the cyber threats are ideal victims for cybercrime that once again uses malware to exploit user’s vulnerabilities. In the social networking the fundamental factor is use of social engineering techniques to circumvent users that most often are redirected on compromised web sites through the sharing of “malicious hyperlink”.
Due the importance of social networks, mine of information, they represent a privileged target for cyber criminals that intend implements new fraud schema and governments that try to spread malware with cyber espionage purpose. Recently the experts of Trusteer firm have discovered a new variant Zeus malware responsible for a series of attacks against principal internet service providers. The variant carried out attacks using the P2P network architecture targeting users of Facebook, Hotmail and Yahoo and Google Mail. Zeus Trojan is born as an agent able to steal banking information by logging keystrokes and form grabbing, it is spread mainly through phishing and drive-by downloads schemes.
The malware variant that hit Facebook uses a web injection mechanism to propose to the victims a special price reduced of 20% for purchases made with Visa or MasterCard debit card using their Facebook account. The scam promises in fact that after registering debit card information, the victim will earn cash back when they purchase Facebook points. Of course to the user is proposed a form for the registration of debit card info that is equivalent to a legitimate one also in term of proposed layout
Who is responsible for malware diffusion?
Use of malware is really frequent for different purposes, cybercrime, cyber warfare, hacktivism, governments monitoring and surveillance.
The criminal organizations are very active in the development and diffusion of malware, is known that this kind of crime is very profitable and often go unpunished due lack in current regulation in many country of the world. Criminal gangs have discovered how much lucrative is the cybercrime and how reduced are the possibility to be legally pursued. Computer crime by its nature has placed in the cyberspace with direct effects on the real world, but due this characteristic, its persecution is virtually impossible for the absence of globally shared regulations against this type of illicit.
Main use of malware made by cyber criminals are Malware could be used in different fraud patterns, mainly their use is to steal user sensible information like banking credentials. The diffusion could happen through several channels like social networking, mail spamming, visiting infecting host or hijacking web navigation. The common factor is the identity theft of the user for fraudulent activity. During the last weeks we have assisted to the rapid diffusion of new generations of Ransomware demonstrating that the use of malware could be adapted for different model of cybercrimes.
Ransomware is a type of malware which restricts access to the computer resources of the victim demanding the payment of a ransom for the removal of the restrictions. To prevent the access to the resources the malware encrypt files of infected machine.
Cybercrime is not only the sector that adopts malware for its purposes, one of the most interesting usage is related to cyber warfare. Borrowing definition of “cyber weapon” provided by security experts Thomas Rid and Peter McBurney :
“a computer code that is used, or designed to be used, with the aim of threatening or causing physical, functional, or mental harm to structures, systems, or living beings“
we can immediately think to the effect of a computer malware targeted against a strategic objective such as a critical infrastructure.
Over the years many cyber weapons have been identified as described the most famous of which is the virus Stuxnet, for its development is common opinion that has been involved, by US and Israel Governments, a pool of high specialists. The reality is more complex, the future for malware in cyber warfare scenario is made of dedicated platform used to create multiform and modular agent that could target specific objectives simply including new components. We are facing with open projects that evolve with the need and in function with specific targets present new offensive features.
Kaspersky’s director of global research & analysis, Costin Raiu, discovered with his team the existence of a common platform to build the malwares Duqu and Stuxnet, that they named “Tilded platform” because many of the files in agents have names beginning with the tilde symbol “~” and the letter “d.””. What is really interesting is that the researcher is convinced that the same framework has been also used to create at least three other pieces of malware confirming the existence of a “factory” platform that Costin Raiu defined using the following statement:
“It’s like a Lego set. You can assemble the components into anything: a robot or a house or a tank,”
But malware could be also the next option of group of hacktivist such as Anonymous. During the last couple of years we have witnessed the escalation of operations conducted by the Anonymous group, the hacker group that is expressing a social dissent through cyber attacks.
Is common conviction that the group use only DDoS attacks for its operations, but the collective is changing and some security experts believe that they are also exploring other options such as malware deployment. The purposes of malware usage maybe be different, malicious software could be used to attack strategic objectives with targeted campaign and also to conduct cyber espionage operations. Also DDoS attacks could be automated infecting machines of the victims or simply hosting a malware on a website that redirect the attacks against the chosen targets.
Another regrettable usage of malware is monitoring and controlling, typically implemented by governments and intelligence agencies. In most cases virus and trojan have been used to infect computer used to attack dissident, opponents and political oppositions. The purpose is to track their operation on the web, gather sensible information and localize them. In many cases the use of malware has made possible the capture of the victims and their ruthless suppression.
During the
Syrian repression the government has discovered that dissidents were using program such as Skype to communicate, so it has used the same channel to spread the backdoor “Xtreme RAT”, a malware that belong to the Remote Access Tool category really simple to retrieve on line at a low price (Full version Price: €100 EUR).
Cyber espionage malware, a global nightmare
Malware once were used primarily to destroy the victim’s PC, but the scenario has completely changed today.
We have seen that cyber criminals, governments, and groups of
hacktivists, with different purposes, tend to lean toward the spread of malicious agents that have the capacity to infiltrate the targets be silently stealing from them the most information. Profit, Power, Protest the main motivations behind the attacks, that are radically changing user’s approach to the web and the their perception of security.
We usually blame
China but recent events have shown that it is common practice to use malware with these purposes, but China is not the only nations involved in similar attacks, let’s consider for example United States and researches to develop cyber weapon that are able to infiltrate sensitive networks to steal information. The project
Olympic Games is the evidence of the effort spent in this new form of offense, and other valid examples of malware used with cyber espionage purpose are
Duqu and
Flame both developed to gather sensible information from Iranian Government.
A recent study on cyber-espionage has demonstrated that more than 200 families of malware have been designed and used to spy on government and corporate representatives.
We have assisted to the diffusion of new agents that works in
botnet architectures, in similar way to the ones used by cybercrime for massive attacks, but that are specifically developed for selected targets that resulting to have a minor dimension.
The study reveals that more than 1,100 domain were used in the attacks, in particular the experts have traced the botnet used analyzing the traffic produced, the Sinkholing, a consolidated technique used by many security firms,
Sinkholing is a technique that researchers use to redirect the identification of the malicious C&C server to their own analysis server. With this methods researcher design a map of the botnet and of the control center identifying the type and numbers of final attacks.
Attacks have the primary intent to steal classified information from government agencies or trade secrets from corporations and the situation could be extremely dangerous for the economy of a company and of the overall country.
With similar attacks governments and business try to reduce the technological gap with their competitors, it’s clear how much diffused is the phenomenon.
The
cybercrime is not watching, it has increased focus in targeting individuals and organizations of all sizes to steal financial information, in particular under pressure has made the small businesses too vulnerable to cyber attacks.
The Trend Micro has reported a sensible increase of focused attacks respect previous quarter (27%), around 142 million threats which were blocked from infecting small businesses but also large companies have been hit by the crime as happened for the IXSHE campaign.
Cyber espionage represents a serious cyber threat, and government agencies are defining best practices to reduce the risk of exposure to the attacks.
NIST has recently released the public comment release of Draft Special Publication 800-83 (SP) Revision 1,
Guide to Malware Incident Prevention and Handling for Desktops and Laptops.
Malware is considered the most common external threat to most hosts, causing widespread damage and disruption and necessitating extensive recovery efforts within most organizations.
This publication provides recommendations for improving an organization’s malware incident prevention measures. It also gives extensive recommendations for enhancing an organization’s existing incident response capability so that it is better prepared to handle malware incidents, particularly widespread ones.
Which future for malware?
The data collected on the malware diffusion let us think that new sophisticated agents will be developed in the short term, most of them able to exploit also 0-days vulnerabilities.
We must expect that governments and intelligence agencies will make large use of malicious computer program to infiltrate enemy network and steal sensible information, we are in the cyber era and this is the new way to fight. The conflict are moving from the ordinary world in the cyber space, new powerful cyber weapon could be designed to attacks critical infrastructure and left in the wild to spread it self-making serious damages.
One of the most critical aspect in fact is the ability of malware developer to follow the evolution of their creation, there is the concrete risk that virus and rootkit are reverse engineered to create new aggressive agent that could be freely sold to best bidder.
Another trend that create great concern is related to the botnet diffusion and evolution, the traditional techniques used to detect and decapitate the malicious structure are becoming obsolete due the introduction of new sophisticated structure. Let’s think to P2P botnet or to botnet that doesn’t need the traditional presence of Command and Control server, characteristic that make hard their detection.
Factors like the massive diffusion of mobile devices and the integration of new services, such as banking and communication, in social networking platform are creating the right condition for the diffusion of malicious cyber threats. Consider also the increasing attention of ordinary crime in cyber fraud, a business relatively secure that will attract capitals in cybercrime areas, new groups of hackers and specialist could sell their services to the crime with unpredictable consequences.
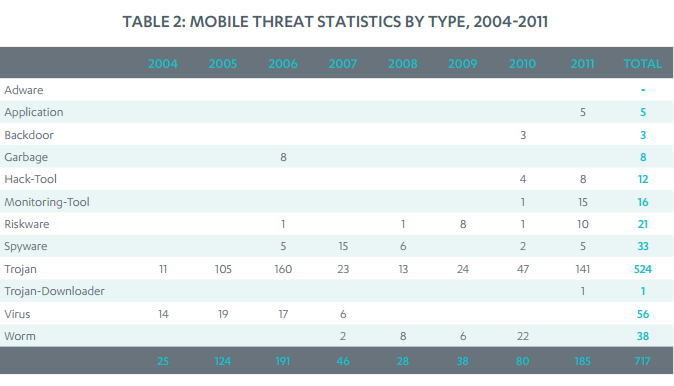
To give an idea on how much attractive is the mobile technology for malware developer let’s give a look to the
Mobile Threat Report released by security firms F-Secure that warns of a dramatic increase in malware targeting mobile devices, especially Androind OS based. The following table reports interesting statistics on mobile threats discovered between 2004 and 2011, showing an impressive growth grouped by malware type.
Figure 2 – F-Secure – Mobile Threat Report
According the report “In Q1 2011, 10 new families and variants were discovered. A year later, this number has nearly quadrupled with 37 new families and variants discovered in Q1 2012 alone,” the report states.”
Conclusions
All this data show a situation can only worsen in the next future, to mitigate the risks related to malware diffusion it’s necessary to increase the level of awareness especially for those sectors more exposed such as mobile and social networking.
rtechinsane,
icodesource,
SEO,
SEO Tips,
SEO Backlinks,
SEO content,
SEO tricks,
SEO Engine,
codes,
gadgets,
iphones,
ipad,
4G phones,
geeks,
reviews,
database,
DBMS,


 In about six weeks, the InterWebs will flood with posts commemorating a tech visionary's passing.
In about six weeks, the InterWebs will flood with posts commemorating a tech visionary's passing.